Introduction
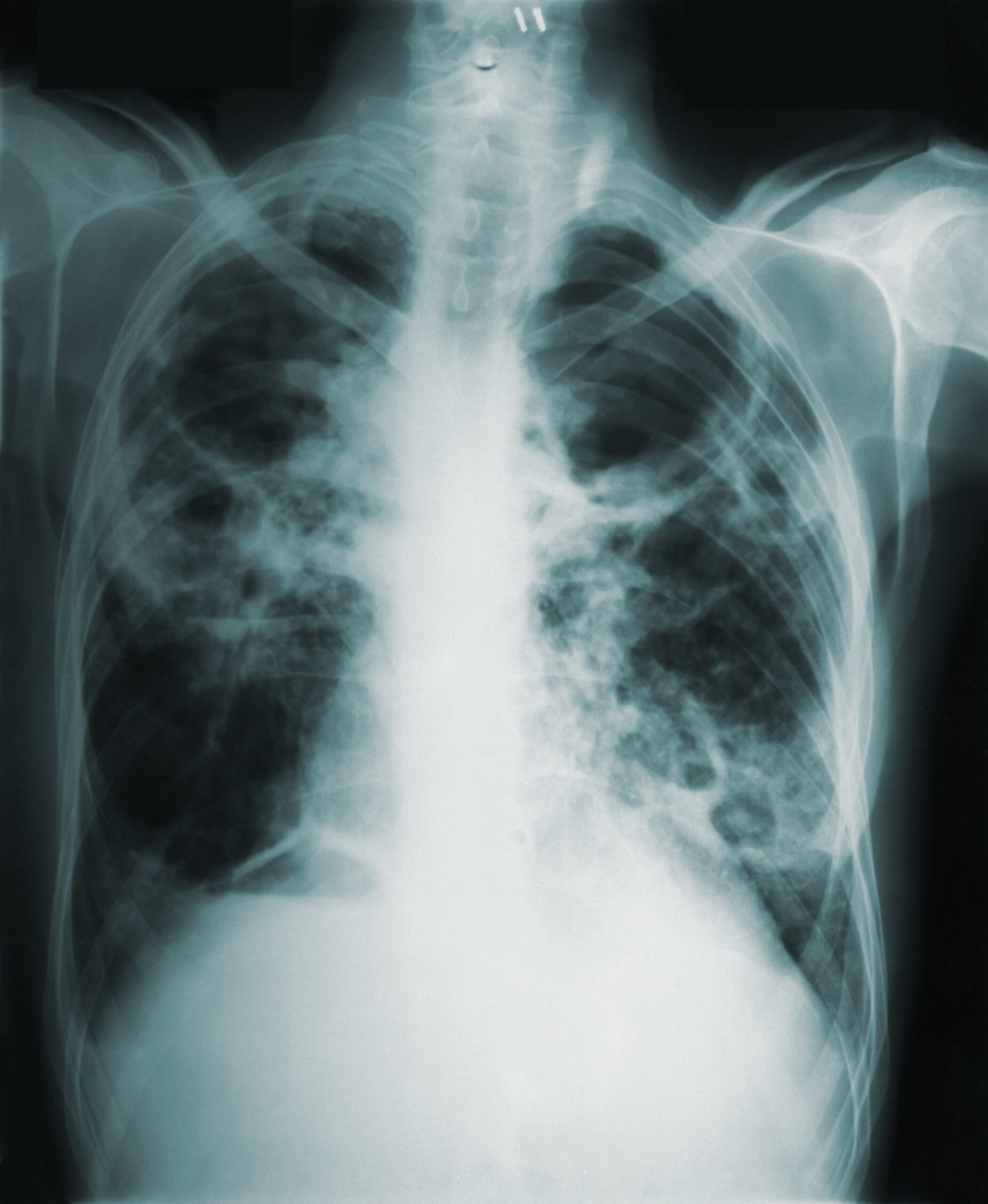
Pulmonary fibrosis is a chronic and progressive lung disease characterized by the thickening and scarring of the lung tissue. This condition hampers the normal functioning of the lungs, making it difficult for individuals to breathe properly. In this article, we will delve into the causes, investigations, treatment options, and drugs available for pulmonary fibrosis.
Causes of Pulmonary Fibrosis
The exact cause of pulmonary fibrosis is often unknown, and it is referred to as idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) in such cases. However, there are several factors that can contribute to the development of pulmonary fibrosis, including:
1. Environmental factors: Exposure to certain environmental pollutants, such as asbestos, silica dust, and certain chemicals, can increase the risk of developing pulmonary fibrosis.
2. Genetic factors: In some cases, pulmonary fibrosis can be inherited, suggesting a genetic predisposition to the disease.
3. Autoimmune diseases: Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, and scleroderma have been linked to an increased risk of pulmonary fibrosis.
4. Medications: Certain medications, such as chemotherapy drugs and some antibiotics, can cause lung damage and lead to pulmonary fibrosis.
Investigations for Pulmonary Fibrosis
When diagnosing pulmonary fibrosis, healthcare professionals may recommend a series of investigations to confirm the presence of the disease and determine its severity. These investigations may include:
1. Pulmonary function tests: These tests measure lung capacity and the efficiency of gas exchange, providing valuable information about the functioning of the lungs.
2. High-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) scan: HRCT scans provide detailed images of the lungs, helping to identify any abnormalities or scarring.
3. Bronchoscopy: This procedure involves inserting a thin tube with a camera into the airways to visualize the lungs and collect samples for further analysis.
4. Lung biopsy: In some cases, a small sample of lung tissue may be obtained through a biopsy to examine it under a microscope and confirm the presence of fibrosis.
Treatment Options for Pulmonary Fibrosis
While there is no cure for pulmonary fibrosis, various treatment options can help manage the symptoms and slow down the progression of the disease. These treatment options may include:
1. Medications: Certain medications, such as corticosteroids and immunosuppressants, may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and slow down the scarring process in the lungs.
2. Oxygen therapy: Supplemental oxygen can help improve breathing and alleviate symptoms, especially during physical activity or sleep.
3. Pulmonary rehabilitation: This comprehensive program includes exercises, breathing techniques, and education to improve lung function and overall quality of life.
4. Lung transplantation: In severe cases, where other treatment options have failed, a lung transplant may be considered as a last resort.
Drugs for Pulmonary Fibrosis
Several drugs have been approved for the treatment of pulmonary fibrosis, with the aim of slowing down the progression of the disease and improving symptoms. These drugs include:
1. Pirfenidone: This medication reduces the production of collagen, a protein that contributes to lung scarring.
2. Nintedanib: Nintedanib targets specific signaling pathways involved in the scarring process, helping to slow down disease progression.
It is important to note that these drugs may not be suitable for everyone, and their usage should be discussed with a healthcare professional.
Conclusion
Pulmonary fibrosis is a complex lung disease that requires careful management and treatment. By understanding the causes, undergoing appropriate investigations, and exploring available treatment options and drugs, individuals with pulmonary fibrosis can work towards improving their quality of life and slowing down the progression of the disease. If you suspect you may have pulmonary fibrosis, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan.