Definition
Crohn’s disease (CD) is a chronic, idiopathic, transmural inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that can affect any part of the gastrointestinal tract, most commonly the terminal ileum and colon, characterized by skip lesions and granulomatous inflammation.
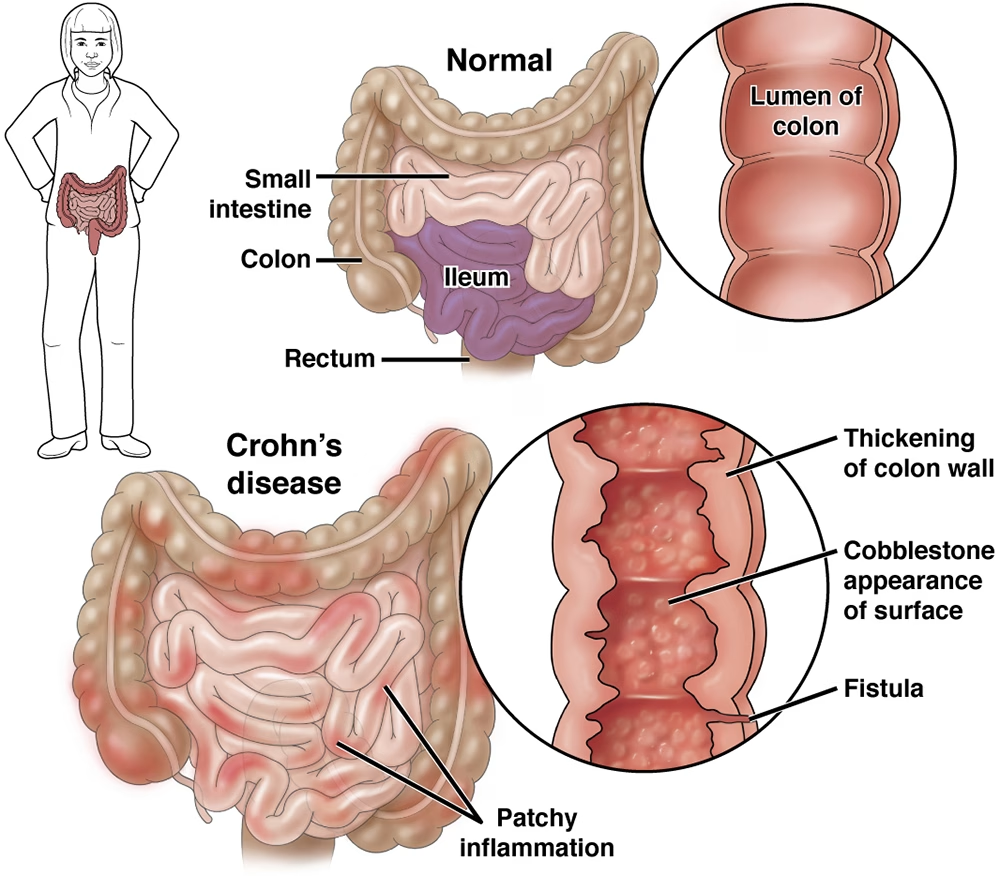
Clinical Picture
Symptoms
- Gastrointestinal:
- Chronic diarrhea (often non-bloody)
- Abdominal pain (typically right lower quadrant)
- Weight loss and fatigue
- Low-grade fever
- Possible obstructive symptoms (colicky pain, distension, vomiting)
- Perianal disease:
- Fistulas, fissures, abscesses, skin tags
- Extraintestinal manifestations (EIMs):
- Musculoskeletal: Arthritis, sacroiliitis, ankylosing spondylitis
- Dermatologic: Erythema nodosum, pyoderma gangrenosum
- Ocular: Uveitis, episcleritis
- Hepatobiliary: Primary sclerosing cholangitis, fatty liver
Diagnosis & Investigations
1. Laboratory Tests
- CBC: Anemia, leukocytosis, thrombocytosis
- CRP, ESR: Elevated (disease activity markers)
- Albumin: Low in severe disease
- Fecal calprotectin or lactoferrin: Elevated → marker of intestinal inflammation (useful for screening and monitoring)
- Exclude infection: Stool cultures, ova & parasites, C. difficile toxin/PCR
2. Endoscopy
- Ileocolonoscopy with biopsy → gold standard
- Findings: aphthous ulcers, linear/serpiginous ulcers, cobblestoning, skip lesions, strictures
- Histology: noncaseating granulomas (pathognomonic but present in <30%)
- Upper GI endoscopy if proximal involvement suspected
3. Imaging
- MR enterography (preferred) or CT enterography for small bowel involvement and complications:
- Detects strictures, fistulas, abscesses, and transmural inflammation
- Pelvic MRI for perianal fistulizing disease
4. Other
- Capsule endoscopy: useful for small bowel lesions if no strictures (after patency capsule)
- Ultrasound (in experienced hands) for bowel wall thickening and vascularity
Treatment Lines (Stepwise, Based on Severity and Site)
General Principles
- Induce remission → Maintain remission
- Avoid corticosteroids long-term
- Tailor therapy to disease phenotype: inflammatory, stricturing, or penetrating
1. Induction of Remission
| Severity | Therapy |
|---|---|
| Mild–Moderate (Ileal/Right colonic) | Budesonide 9 mg/day (controlled ileal release) for up to 8–12 weeks |
| Moderate–Severe (Extensive or refractory) | Systemic corticosteroids (Prednisone 40–60 mg/day taper) |
| Steroid-refractory/dependent or high-risk | Biologic therapy (Anti-TNF, Anti-IL12/23, Anti-integrin) ± immunomodulator |
2. Maintenance of Remission
| Agent | Notes |
|---|---|
| Immunomodulators: Azathioprine, 6-MP, Methotrexate | Effective for maintaining remission; not for induction |
| Biologics: | Preferred for moderate–severe or refractory disease |
| – Anti-TNF: Infliximab, Adalimumab, Certolizumab | Especially for fistulizing disease |
| – Anti-Integrin: Vedolizumab | Gut-selective, safer long-term |
| – Anti-IL12/23: Ustekinumab | Effective for both induction and maintenance |
| – JAK inhibitors (Upadacitinib) | Newer oral option for moderate-severe CD (FDA 2023) |
| Budesonide / Mesalamine | Limited or no role in maintenance (esp. mesalamine ineffective for CD) |
3. Management of Complications
- Strictures: Endoscopic balloon dilation or surgery
- Fistulas: Anti-TNF ± antibiotics (metronidazole, ciprofloxacin)
- Abscess: Drainage + antibiotics (before biologic therapy)
- Perianal disease: MRI evaluation + multidisciplinary approach (surgery + anti-TNF)
4. Supportive Care
- Nutrition: Correct deficiencies (iron, B12, vitamin D, folate, calcium)
- Lifestyle: Smoking cessation (smoking worsens CD)
- Vaccinations: Influenza, pneumococcal, hepatitis B, HPV (before immunosuppression)
- Bone health: Monitor with long-term steroids
Monitoring
- Clinical assessment: Symptoms, quality of life
- Biochemical: CRP, fecal calprotectin
- Endoscopic: Mucosal healing (within 6–12 months after therapy)
- Imaging: As needed for transmural activity
Other Articles :